The Office of the (Near) Future: Remote-First Work
Bhavik Modi | Associate Director at BTS Innovation & Digital Transformation
Bryan Campbell | Agile Transformation Coach & President of 7 C’s Consulting
Leaders have been surprised at how productive employees have been working from home, many are considering how to accelerate a transition already occurring to a remote-first work environment.
What lessons can we learn from businesses that were intentionally built to be remote-first or are planning a shift to an office culture focused on virtual work?
Reimagining the Office
“If I had asked people what they wanted, they would have said faster horses.”
– Henry Ford
As human beings, it is difficult for us to think about the future without viewing it as an incremental improvement over the present. As Henry Ford pointed out, busting our biases is hard and we’re seeing this as companies have been forced to transition into virtual work environments. Employees have resorted to simply recreating everything that was happening in an office and doing it online. This isn’t an uncommon problem and we’ve seen it many times before, in fact there have been many such step changes in history, take films for example:
- When movies were first created, they were essentially plays on a screen with the video camera remaining static similar to an audience member watching a play– moviemaking only came about as mental models shifted and filmmakers explored new ideas such as moving the camera[1]
- In 1928, Joseph Schenck, the President of United Artists told the New York Times, “talking doesn’t belong in pictures…I don’t think people will want talking pictures long”. The common wisdom at the time (since they had never experienced films with dialogue) was that talkies (as talking-films were called) were simply a gimmick. Only after audiences adjusted and audio-recording technology improved, was dialogue in movies embraced as we see today.[2]
If you are a leader considering a shift to a remote-first workplace, you have to embrace two types of disruption. The first is reactionary, reacting to a disruption like COVID-19 that happens to you and your business. The second type of disruption is proactive, often referred to as creative destruction[3] – deliberately breaking down existing ways of working to make space for innovation. Most leaders are often good at managing reactionary disruptions or “fire drills” (with COVID-19 fire being a five-alarm type). They are adept at processing data and bring decades of experience in making the hard decisions that are required in these periods. However, proactive disruption is typically more challenging. Leaders have to look past their own well-formed experiences and consider unconventional approaches that are going to feel unfamiliar and uncomfortable.
Our present environment offers an opportunity for you as a leader to lead disruption. Fortunately, the principles are simple and stem from the world of design thinking.
- Define the problem to be solved, build empathy of users (in this case employees),
- Ideate on potential solutions,
- Refine these ideas into those you wish to pursue and then
- Take an agile approach to experimenting with the implementation of these ideas (testing the ideas fast and cheap).
However, this isn’t an article on design thinking so for now let’s focus on common questions that arise when shifting to remote-first work and build on ideas from other companies who were built to be or are transitioning to be remote-first.
What should we do with the Latte Machine in our Corporate HQ?
Employers have invested significant sums of money in corporate campuses that create spontaneous collisions between employees who do not work in the same department. Steve Jobs famously designed Pixar’s campus and later Apple’s campus with the intent to create these interactions. Open offices have also come into vogue made famous by tech startups out of Silicon Valley, where CEOs like Mark Zuckerberg ditched their office to sit with team members and other traditional firms have opted for “hoteling” to create more informal, flexible work environment. As companies have invested more in keeping people engaged at the office via gyms, cafeterias, expresso machines and endless snacks – leaders are left wondering how to walk away from these major investments and what takes their place?
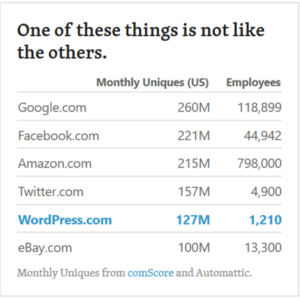 There are two approaches we have seen with remote-first companies, and you’ll notice we say remote-first not remote-only. The first approach is for companies to repurpose their office environment as a co-working space for employees to collaborate with each other when an in-person meeting is required. This requires some thoughtful consideration on what types of interaction make more sense to occur in person and which interactions can happen asynchronously, over the phone or over a video chat. A great example to look at is Automattic – a distributed company with over 1200 Automatticians spread across 77 countries (and 93 different languages. They are behind popular publishing and internet platforms like Tumblr and WordPress and are incredibly productive.
There are two approaches we have seen with remote-first companies, and you’ll notice we say remote-first not remote-only. The first approach is for companies to repurpose their office environment as a co-working space for employees to collaborate with each other when an in-person meeting is required. This requires some thoughtful consideration on what types of interaction make more sense to occur in person and which interactions can happen asynchronously, over the phone or over a video chat. A great example to look at is Automattic – a distributed company with over 1200 Automatticians spread across 77 countries (and 93 different languages. They are behind popular publishing and internet platforms like Tumblr and WordPress and are incredibly productive.
“People are surprised when I say this, but I think in-person is really key. And so we just flip it, so instead of saying you have to be around your colleagues 48 weeks of the year and do whatever you want for a month, we say be wherever you want for 48 weeks out of the year and for three or four weeks a year we’re going to bring you together.” -Matt Mullenweg (Automattic CEO)
The leadership lesson here for remote-first companies is simply to set clear expectations and guidelines for when teams should come together (in a corporate co-working space, coffee shop or elsewhere) and limit those interactions to those that are absolutely necessary – flipping the old co-location ratio like Automattic has done. COVID-19 has challenged our biases of where work can be done most productively and you’ll find that teams (equipped with the right tools and resources at home) can be surprisingly productive without being co-located. And who says you can’t have office perks while at home? It could be as simple as repurposing the money invested in your latte machine and providing a stipend for a green screen, dual monitors, microphone and a high-quality web camera (and an UberEats subscription for some snacks when desired).
How will I know who is working and get facetime with leaders?
“In most companies, it is a significant career advantage to work from the headquarters rather than to work remotely. People in positions of power have a tendency to bias toward giving out opportunities to those whom they are familiar with. Employees in headquarters often don’t keep remote workers front of mind.” – Adam D’Angelo (CEO of Quora)
 Face time with senior leaders is often considered an important right of passage for corporate cultures, the more time a leader spends communicating with you the better chance you have of being noticed for a promotion or a high-impact project. In a remote-first organization you have the opportunity to create a level playing field for a distributed workforce that rewards outcomes and not being the first one in, last one out or sending emails at all times of the day.
Face time with senior leaders is often considered an important right of passage for corporate cultures, the more time a leader spends communicating with you the better chance you have of being noticed for a promotion or a high-impact project. In a remote-first organization you have the opportunity to create a level playing field for a distributed workforce that rewards outcomes and not being the first one in, last one out or sending emails at all times of the day.
The first leadership step in a remote-first organization is to change your work pattern to be remote-first. You can’t be in the office while the rest of your company is remote – otherwise high achievers will follow suit to get facetime with you. Quora’s CEO, Adam D’Angelo has clearly stated in their remote-first announcement that he and his leadership teams will not be located in the office. By being remote yourself, it allows you to shift your talent evaluation and work process to balance towards evaluating the outcomes of a remote workforce.
The second leadership step is to build a new asynchronous rhythm of doing business. Instead of emails and calls (which in a distributed workforce are tough to schedule across time zones) – consider a blogging system like what Automattic uses called P2s to document progress on projects. P2s are posts written every day by employees to summarize what they have been working on, the problems that they might have encountered and the discussions that they had that day. If you think about the purpose of our in-person meetings, whether in person or on Zoom, this is typically what we are doing – unearthing hidden information from our organization to see what folks are working on, reach group decisions and find ways to collaborate. By documenting what is happening on P2s, it has become a cultural norm at Automattic for all employees to read P2s and uncover what is happening around the company. This communication method creates a transparent organization where you don’t have FOMO (fear of missing out) for not being included in a meeting or not being copied on an email chain. Using their internal search index you can look up P2s and follow certain topics (like Google Reader) to stay informed on progress.
The two leadership lessons to take away from this are that if you are going remote-first, your leadership team must model the way and be remote yourselves and that you need to build new communication habits in your organization to allow for asynchronous collaboration and updates.
What about the corporate culture our employees know and love?
 If we were to do a thought experiment and ask you as a leader, what makes your culture great, we would likely get a range of responses from company to company. Some companies value a strong safety and compliance culture that enables them to de-risk their work environment, others value an entrepreneurial environment where they are afforded creativity to take on challenges – it varies but when you check Glassdoor for what makes a company great the office perks are rarely at the top of the list. It’s about the people, work environment and opportunities provided.
If we were to do a thought experiment and ask you as a leader, what makes your culture great, we would likely get a range of responses from company to company. Some companies value a strong safety and compliance culture that enables them to de-risk their work environment, others value an entrepreneurial environment where they are afforded creativity to take on challenges – it varies but when you check Glassdoor for what makes a company great the office perks are rarely at the top of the list. It’s about the people, work environment and opportunities provided.
Those same interactions can be reimagined (not recreated) in a remote-first environment. It could be as simple as creating space on employees calendars for “making time”[4] – consider the first half of each day (up to 12:30 PM) as a time where meetings are not allowed and employees have time to do deep project work. If you reduce the need for emails and check-in calls, it creates more dedicated work time for employees to creatively solve challenges. You can also support small team or 1:1 interactions amongst employees by providing gift cards for lunch or coffee so employees located near each other can meet and network. Another option is for leaders to participate in targeted, fun interactions across the company – for example at BTS we just did a virtual trivia night, a virtual scavenger hunt and invited kids onto a company-wide Zoom call. Anything to create a familial environment – which luckily being stuck in our new “home offices” surrounded by new barking co-workers has already allowed us to do. Remote-first work allows you to memorialize and celebrate what made your office culture great, and re-invest time and resources to progress that culture forward in a distributed work environment.
Keep in mind that many employees will be shifting to working in a home office for the first time and might not have a separate space available dedicated exclusively for work. As a leader, it is important to promote a separation of “church and state”, allowing employees to turn off notifications and step away from their desks. For example in Slack, the default setting is for notifications to be turned on at 8:00 AM and turned off at 6:00 PM based on the time zone – this should be encouraged across all communication channels during core working hours. This is something that organizations and teams must discuss to create formalized working agreements and establish new norms.
Practical Next Steps
As you plan your work environment of the future, consider a few of the practical steps we shared above.
- Reimagine don’t recreate: List out the assumptions you have about in-person work and provoke each one of them, reimagine what those tasks and activities might look like in a virtual work environment.
- Lead the change: If leaders are still in the office, the rest of the company will aim to come into the office – if you want to be remote-first, leaders must commit to being remote themselves
- Flip the ratio of in-person to virtual interactions: In-person interactions don’t go away in a remote-first world, they are more targeted and thoughtful. Provide stipends to employees for team meetings, 1:1s and other interactions and set guidelines on when in-person interactions should happen and when they are not needed.
- Create a new rhythm of communication – asynchronous communication involves a new communication rhythm, repurpose emails/check-ins and other meetings and create new norms for how information is communicated and how others can contribute to building on ideas from other parts of the company
- Memorialize and progress your culture: Continue to honor what makes your culture great, remote-first doesn’t mean you have to lose it – it offers new opportunities to build your culture and invite more talent into your organization that you previously may not have had access to.
——————————————
[1] Source: Stratechery, Ben Thompson Interview with Matt Mullenweg
[2] Source: Vox, https://www.vox.com/2015/2/9/8004661/fads-inventions-changed-world
[3] Source: The Library of Economics and Liberty, https://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/CreativeDestruction.html